Ransomware has changed quite a bit over the past few years—and not in a positive way. What used to be a problem primarily for large companies has now become a daily threat for small and mid-sized businesses everywhere. Attackers are getting faster, smarter, and are using tools that make their jobs easier while making your defenses harder to trust.
If you’re running or managing a small to mid-sized business, this is important. The way ransomware operates today is very different from what most people think. The more you know about what’s really happening, the better prepared you’ll be to protect your business.
If you’re running or managing a small to mid-sized business, this is important. The way ransomware operates today is very different from what most people think. The more you know about what’s really happening, the better prepared you’ll be to protect your business.
Ransomware Has Evolved.
It’s More Aggressive Than Ever!
The ransomware we’re dealing with in 2026 isn’t just the usual “lock your files and ask for money” game anymore. Attackers have turned it into a full‑blown business model — and they’re running it like one.
So, what’s different now?
So, what’s different now?
Attackers are stealing your data before they lock anything.
This gives them a powerful advantage, even if you have backups. They’ll threaten to leak your customer information, financial records, or internal documents unless you pay up.
AI is powering up most of the attacks.
Hackers are using AI to create believable emails, search for weaknesses, and infiltrate accounts faster than most companies can respond.
Attacks happen faster.
What used to take days can now be done in just a few hours. Once they gain access, they operate quickly and quietly.
Ransomware groups are on the rise.
Instead of just a few large organizations, there are now countless smaller groups. They’re tougher to monitor, more unpredictable, and significantly more active.
Why SMBs Are Now The #1 Target
Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) have emerged as the primary targets for ransomware groups, a trend that is surprising to many business owners. This shift is primarily attributed to a combination of opportunity and pressure.
SMBs possess valuable data—such as customer information, financial records, invoices, contracts, and employee data—that can attract attackers. The loss of this sensitive information can significantly disrupt operations.
However, SMBs often lack the robust protection measures that larger companies have in place. This isn’t because they don’t care about cybersecurity; it’s more about the countless responsibilities they juggle, which can make it tough to put in place thorough security measures.
SMBs possess valuable data—such as customer information, financial records, invoices, contracts, and employee data—that can attract attackers. The loss of this sensitive information can significantly disrupt operations.
However, SMBs often lack the robust protection measures that larger companies have in place. This isn’t because they don’t care about cybersecurity; it’s more about the countless responsibilities they juggle, which can make it tough to put in place thorough security measures.
We’re looking at a few key problems:
- No IT support or lack of IT staff
- Not fully configured & outdated security tools
- Remote workers using their personal devices
- Cloud applications that aren't securely set up
- No ongoing security training for employees
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are prime targets for attackers, who see them as a strategic choice due to their high value and relatively low defenses. This combination presents a golden opportunity for easy financial gain.
Hackers know that SMBs are often under significant financial pressure, and when faced with extended downtimes, they can suffer major operational disruptions. Because of this, these businesses are more willing to pay a ransom to quickly restore their services. Additionally, since SMBs are frequently tied to larger companies, they can serve as gateways for attackers aiming to reach bigger targets. This interconnectedness makes SMBs even more attractive to cybercriminals.
Hackers know that SMBs are often under significant financial pressure, and when faced with extended downtimes, they can suffer major operational disruptions. Because of this, these businesses are more willing to pay a ransom to quickly restore their services. Additionally, since SMBs are frequently tied to larger companies, they can serve as gateways for attackers aiming to reach bigger targets. This interconnectedness makes SMBs even more attractive to cybercriminals.
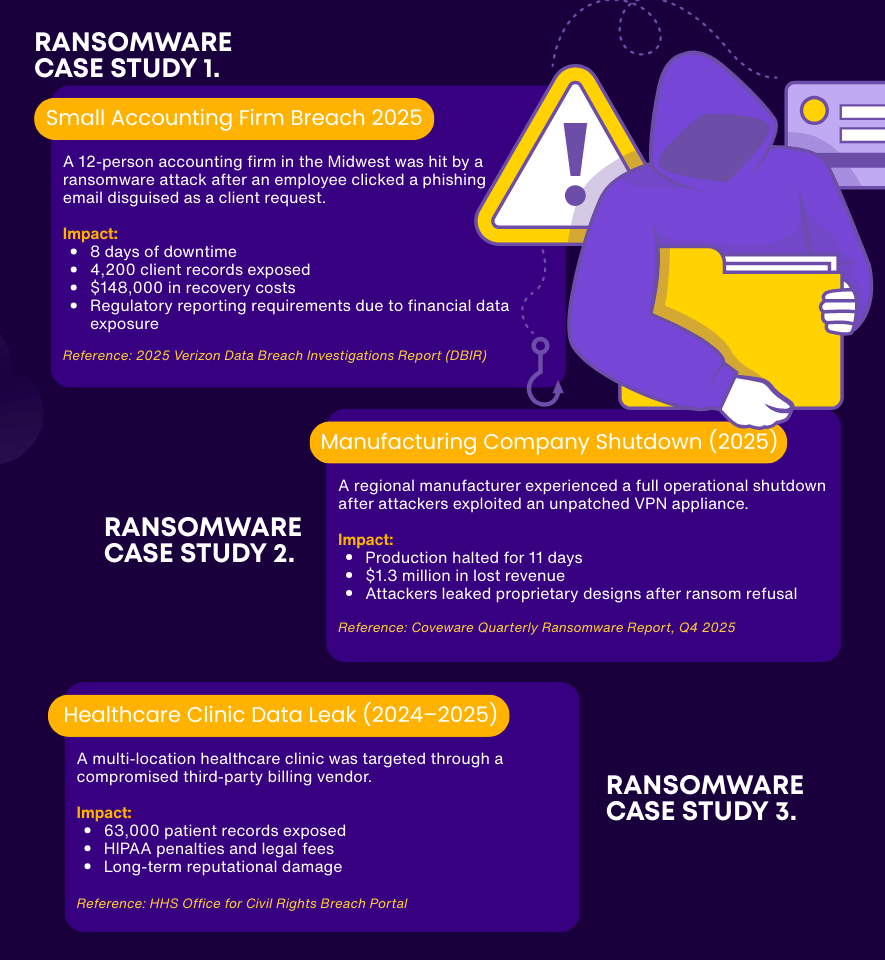
Real Case Studies: How Ransomware Is Hitting Businesses Like Yours
The Essential Steps to Prepare
Your Business in 2026
Ransomware attacks keep increasing, but businesses have the power to take proactive steps to avoid being easy targets. By raising awareness and adopting strategic measures, organizations can significantly lower their vulnerabilities and stay resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Preparation is key, serving as the first line of defense against potential ransomware attacks.
Preparation is key, serving as the first line of defense against potential ransomware attacks.